Adapting to the New Normal: EAPs and the Remote Work Revolution

The COVID-19 pandemic marked a significant shift in the way we work, accelerating the adoption of remote work across various industries. As countries implemented lockdowns and social distancing measures, organizations worldwide quickly adapted by transitioning their employees to remote work arrangements. This shift was driven by the necessity to maintain business continuity while ensuring the safety and health of employees.
Key Points:
- Rapid Transition: Companies of all sizes and sectors had to swiftly implement remote work setups, often without prior preparation or infrastructure.
- Global Impact: The pandemic made remote work a global phenomenon, affecting millions of workers simultaneously.
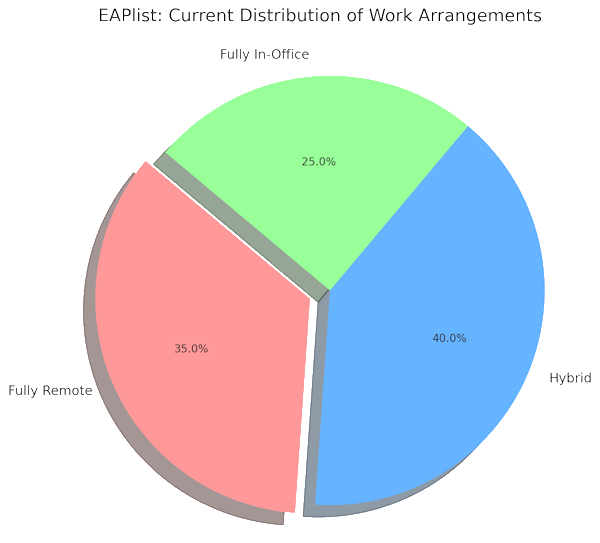
- Lasting Changes: What began as a temporary solution has now led to lasting changes in work culture, with many organizations continuing remote or hybrid models even as restrictions ease.
Introduction to Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs)
Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) are employer-sponsored programs designed to support employees’ well-being, offering confidential services that address various personal and work-related issues. These programs have long been a critical resource for employees, providing access to counseling, legal assistance, financial advice, and more.
Key Points:
- Comprehensive Support: EAPs typically offer a wide range of services, including mental health counseling, stress management, and crisis intervention.
- Confidentiality: One of the core features of EAPs is the confidentiality of the services, encouraging employees to seek help without fear of stigma.
- Accessibility: EAPs are often available 24/7, making them accessible to employees whenever they need support.
1. The Evolution of Remote Work
Historical Context: The Evolution of Remote Work Over Time
Remote work is not a new concept; it has been steadily gaining traction over the past few decades. However, its adoption was often limited to specific industries and roles that could be performed independently and outside a traditional office setting. Technological advancements, such as high-speed internet, video conferencing tools, and cloud computing, have gradually made remote work more feasible and attractive to both employers and employees.
Key Points:
- Pre-Pandemic Remote Work: Before the pandemic, remote work was often seen as a perk or a flexible option for certain employees, rather than a standard practice.
- Technological Enablers: The growth of digital tools and platforms made remote collaboration and communication more efficient and effective.
The Sudden Shift to Remote Work During the Pandemic
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in early 2020 forced a sudden and widespread shift to remote work. This transition was unprecedented in scale and speed, with companies and employees having to adapt to new working conditions almost overnight. For many, this shift included setting up home offices, learning to use new digital tools, and managing work in a completely different environment.
Key Points:
- Rapid Adjustment: Organizations had to quickly implement policies and provide resources to support remote work, including hardware, software, and training.
- Challenges and Opportunities: While the transition presented challenges, it also highlighted the potential benefits of remote work, such as increased flexibility and reduced commuting time.
Current State: The Prevalence of Remote and Hybrid Work Arrangements
As the immediate crisis of the pandemic has subsided, remote work has remained a significant part of the work landscape. Many companies have embraced hybrid work models, combining remote and in-office work to offer greater flexibility. This shift reflects a broader change in workplace culture, where remote work is increasingly seen as a viable and often preferred option.
Key Points:
- Hybrid Work Models: The emergence of hybrid work arrangements allows employees to split their time between remote and in-office work, providing flexibility and maintaining team cohesion.
- Employee Preferences: Surveys and studies have shown that many employees prefer the option to work remotely, citing improved work-life balance and productivity.
- Ongoing Adaptation: Companies continue to refine their remote work policies and practices, integrating lessons learned during the pandemic to create sustainable work environments.
2. Challenges Faced by Remote Employees
Isolation and Loneliness
One of the most significant challenges remote employees face is isolation and loneliness. The absence of in-person interactions with colleagues can lead to feelings of disconnection and social isolation, impacting mental health and overall well-being.
Key Points:
- Lack of Social Interaction: Remote employees miss out on the casual conversations and spontaneous interactions that occur in an office setting, which can help build camaraderie and support networks.
- Mental Health Impacts: Prolonged isolation can contribute to anxiety, depression, and a sense of detachment from the workplace community.
- Strategies for Mitigation: Encouraging regular virtual check-ins, team meetings, and social events can help alleviate feelings of isolation.
Work-Life Balance Struggles
Remote work blurs the boundaries between work and personal life, making it challenging for employees to maintain a healthy work-life balance. This can lead to burnout and decreased job satisfaction.
Key Points:
- Blurring Boundaries: The lack of physical separation between work and home life can result in employees working longer hours or having difficulty “switching off” from work mode.
- Increased Workload: Some employees may feel pressured to be more productive or available outside regular working hours, leading to overwork.
- Time Management Challenges: Managing household responsibilities alongside work duties can create additional stress and time management challenges.
Digital Fatigue
With the shift to remote work, employees are spending more time on digital devices, leading to digital fatigue. This phenomenon is characterized by exhaustion and stress resulting from prolonged screen time and constant connectivity.
Key Points:
- Increased Screen Time: The reliance on video calls, emails, and digital communication tools has led to increased screen time, which can cause eye strain, headaches, and reduced productivity.
- Constant Connectivity: The expectation to be constantly available and responsive can contribute to stress and anxiety, making it difficult for employees to unplug and recharge.
- Preventing Burnout: Encouraging regular breaks, setting clear boundaries for work hours, and promoting digital detox practices can help reduce digital fatigue.
3. The Role of EAPs in Addressing Remote Work Challenges
Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) have traditionally played a crucial role in supporting employees’ mental, emotional, and social well-being. With the shift to remote work, the role of EAPs has become even more vital as they adapt to meet the unique challenges faced by remote employees.
Overview of EAP Services
EAPs offer a wide range of services designed to assist employees with personal and work-related issues. These services include mental health counseling, financial advice, legal assistance, and support for substance abuse and other personal crises.
Key Points:
- Confidential Support: EAP services are confidential, providing a safe space for employees to seek help without fear of stigma or repercussions.
- Wide Range of Services: EAPs address various aspects of well-being, from mental and emotional health to practical issues like financial planning and legal concerns.
- Accessibility: EAPs are often available 24/7, offering support at times convenient for employees, including outside regular work hours.
Adapting EAPs to Remote Work Challenges
As remote work becomes more prevalent, EAPs have adapted their offerings to better support employees facing challenges unique to this work arrangement. This adaptation includes expanding digital resources, providing specialized counseling, and offering new types of support tailored to remote work scenarios.
Key Points:
- Digital Expansion: EAPs have increased their digital presence, offering virtual counseling sessions, online resources, and mobile apps to make services more accessible to remote employees.
- Specialized Counseling: EAPs now provide targeted support for issues like isolation, work-life balance, and digital fatigue, recognizing these as common challenges for remote workers.
- Flexible Support Options: EAPs are offering more flexible support options, such as on-demand webinars, self-help tools, and virtual workshops, to accommodate diverse employee needs and schedules.
4. EAP Strategies for Supporting Remote Employees
As remote work continues to evolve, Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) are implementing various strategies to address the specific needs of remote employees. These strategies focus on enhancing mental health support, promoting work-life balance, supporting digital wellness, and fostering virtual social connections.
Enhanced Counseling and Mental Health Support
EAPs have expanded their mental health services to cater to the growing demand among remote employees facing isolation, anxiety, and other mental health challenges.
Key Points:
- Virtual Counseling Sessions: EAPs offer virtual counseling sessions through video calls, phone consultations, and online chat platforms, making it easier for employees to access support from the comfort of their homes.
- Specialized Therapists: EAPs provide access to therapists who specialize in issues related to remote work, such as isolation, digital fatigue, and work-life integration.
- Crisis Support: EAPs have enhanced their crisis support services, offering immediate assistance for employees experiencing acute stress, grief, or other emergencies.
Work-Life Balance Resources
Maintaining a healthy work-life balance is a critical concern for remote employees. EAPs are offering resources and tools to help employees manage their time effectively and set boundaries between work and personal life.
Key Points:
- Time Management Workshops: EAPs conduct workshops and webinars focused on time management techniques, helping employees prioritize tasks and manage their schedules more efficiently.
- Stress Management Techniques: Resources on mindfulness, relaxation techniques, and stress reduction are provided to help employees cope with the pressures of balancing work and home responsibilities.
- Boundary-Setting Guidance: EAPs offer guidance on setting clear boundaries, such as creating a dedicated workspace, setting specific work hours, and communicating availability to colleagues and family members.
Support for Digital Wellness
With the increased reliance on digital devices, EAPs are focusing on promoting digital wellness to help employees avoid burnout and maintain a healthy relationship with technology.
Key Points:
- Managing Screen Time: EAPs provide tips and strategies for managing screen time, such as taking regular breaks, using blue light filters, and setting limits on non-essential digital activities.
- Digital Detox Programs: EAPs encourage digital detox practices, including unplugging from devices during off-hours, engaging in offline activities, and setting aside tech-free times.
- Education on Digital Well-being: Educational resources on the impact of excessive screen time and how to mitigate its effects are offered to employees and their families.
Virtual Social and Community Building Initiatives
To combat isolation and foster a sense of community among remote employees, EAPs are facilitating virtual social interactions and community-building activities.
Key Points:
- Online Support Groups: EAPs organize online support groups where employees can share experiences, offer support, and connect with others facing similar challenges.
- Virtual Team-Building Activities: EAPs collaborate with companies to create virtual team-building events, such as online games, workshops, and social gatherings, to strengthen team bonds and morale.
- Peer Networking Opportunities: EAPs provide platforms for peer networking, enabling employees to connect with colleagues from different departments or locations for professional and social interactions.
As the landscape of work continues to evolve, Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) are stepping up to meet the unique challenges faced by remote employees. By expanding and adapting their services, EAPs play a vital role in supporting mental health, promoting work-life balance, and fostering a sense of community among remote workers. These programs are not only addressing immediate concerns like isolation, digital fatigue, and boundary-setting but are also laying the groundwork for a more resilient and adaptable workforce. As organizations continue to navigate the complexities of remote and hybrid work, investing in and leveraging EAPs will be crucial in ensuring the well-being and productivity of employees. By embracing these changes, companies can create a supportive and inclusive work environment that meets the needs of all employees, regardless of where they work.