Strengthening Resilience: How EAPs Enhance Crisis Management in the Workplace

Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) are essential tools in the management of workplace crises. They provide critical support services that help stabilize the workforce during tumultuous times, ensuring both employee well-being and organizational functionality.
Defining Workplace Crises
A workplace crisis can vary widely but typically involves situations that disrupt normal operations and pose serious threats to employee safety and business continuity. These include:
- Natural Disasters: Events like earthquakes, hurricanes, and floods that can physically damage infrastructure and emotionally impact employees.
- Violence: Incidents such as active shooter situations or assaults within the workplace.
- Mental Health Emergencies: Scenarios where an employee or group of employees face severe psychological distress, potentially leading to acute crises.
Impact of Crises on the Workplace
The impact of such crises is profound and multifaceted:
- Employee Well-being: Crises can lead to significant stress, anxiety, and even trauma among employees, affecting their mental health and overall well-being.
- Organizational Functionality: From operational disruptions to potential financial losses, the ripple effects of a crisis can threaten the very survival of an organization.
EAPs as a Mitigating Force
In crisis situations, EAPs provide immediate and ongoing support. They offer counseling and intervention services to help employees manage their emotional responses to the crisis. Additionally, EAPs can aid in the development of crisis management plans that include psychological health considerations, helping ensure that organizations are prepared for future incidents.
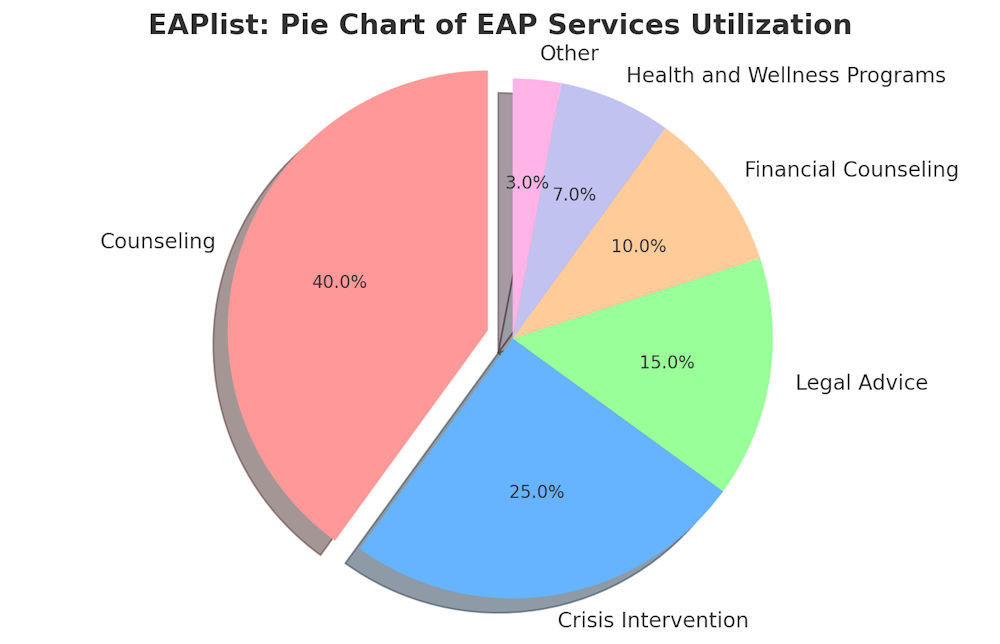
EAPs in Crisis Preparedness
Enhancing Employee Resilience through EAPs
Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) proactively contribute to crisis preparedness by focusing on enhancing the resilience of the workforce. This is achieved through comprehensive training programs that educate employees on recognizing stress signals, employing de-escalation techniques, and practicing mindfulness to maintain calm during crises.
Tailored Training Programs
These training sessions are tailored to the specific needs of the organization and often include simulations or role-playing exercises that help employees experience and respond to crisis scenarios in a controlled environment. By preparing employees for the emotional and psychological challenges of a crisis, EAPs enhance the overall readiness of the organization.
Strategic Development of Crisis Plans
EAP professionals are integral to the strategic development of crisis management plans. They work in conjunction with security experts and organizational leaders to ensure that mental health considerations are embedded within these plans. This collaborative approach helps in crafting protocols that address both immediate and post-crisis mental health needs.
Resource Allocation and Crisis Simulation
EAPs assist in identifying key resources and support systems that should be readily available during a crisis. They also recommend regular crisis simulations to test the efficacy of the plans and to ensure that employees are familiar with the procedures.
Integration with Organizational Culture
The success of any crisis plan depends significantly on its integration into the organization’s culture. EAPs advocate for a culture that prioritizes mental health and safety, promoting an environment where employees feel supported and prepared to handle crises.
Continuous Improvement and Feedback Loops
Effective crisis management requires continuous improvement. EAPs facilitate this by establishing feedback loops where employees can share their experiences and suggestions after training sessions or real crisis events. This feedback is crucial for refining crisis plans and training programs.
EAPs During a Crisis
Immediate Benefits of EAP Activation
Activating an Employee Assistance Program (EAP) during a crisis provides immediate support to employees, helping to manage the emotional and psychological fallout. Key benefits include:
- Rapid Response Counseling: EAPs offer immediate access to mental health professionals who can provide crisis counseling, helping employees to stabilize emotionally after a traumatic event.
- Guidance for Leadership: EAPs support organizational leaders with strategies for effective communication and employee management during crises, ensuring a coordinated response.
Case Studies Showcasing EAP Effectiveness
- Natural Disaster Response: Following a major earthquake, an organization’s EAP provided on-site counseling and virtual support sessions for employees, significantly reducing post-traumatic stress symptoms and facilitating a quicker return to normal operations.
- Violence in the Workplace: After an incident of workplace violence, the affected company’s EAP stepped in immediately to offer psychological first aid and grief counseling. The program’s involvement was crucial in helping employees process the event and preventing long-term psychological impact.
- Handling a Pandemic: During the COVID-19 pandemic, EAPs were instrumental in providing employees with tools for managing anxiety and isolation, which was essential for maintaining workforce morale and productivity in remote work settings.
EAPs in Post-Crisis Recovery
Facilitating Long-Term Healing
After the immediate crisis has passed, EAPs play a crucial role in facilitating long-term recovery and helping employees adjust back to their regular work routines.
Continued Support and Counseling
EAPs provide ongoing counseling to address lingering psychological effects, helping employees cope with trauma and prevent long-term mental health issues. This ongoing support is crucial for full emotional recovery.
Reintegration Programs
EAPs often implement reintegration programs that help employees transition back to work. These programs might include phased returns or modified duties, depending on the nature of the crisis and its impact.
Training and Workshops
Post-crisis, EAPs can offer workshops and training sessions to reinforce coping strategies and resilience-building, ensuring that the workforce is better prepared for future crises.
Feedback and Improvement
EAPs also engage in gathering feedback from employees about the crisis management process. This feedback is essential for improving the existing crisis management plans and ensuring that the strategies are effective and relevant.
The role of EAPs in post-crisis recovery is vital. By providing continued support and resources, EAPs not only aid in the psychological recovery of employees but also strengthen the organization’s overall resilience.
Strengthening Crisis Response through EAP and Organizational Collaboration
Strategic Integration with Organizational Policies
- Unified Approach: Integrating EAP services into the broader crisis management and workplace policies enhances overall response effectiveness.
- Policy Development: Collaborating in the development and refinement of policies that address both preventive measures and reactive strategies.
Collaborative Frameworks for Enhanced Support
- Cross-departmental Coordination: Establishing protocols for cooperation between EAPs and departments like HR, security, and health services.
- Shared Objectives: Aligning the goals of various departments with EAP initiatives to ensure cohesive support during crises.
Role of HR in Maximizing EAP Impact
- Communication Champion: HR departments can lead in promoting EAP benefits, ensuring all employees are aware and understand how to access services.
- Feedback Loop: Facilitate a feedback mechanism where employees can share their experiences with EAP services, which can help tailor future offerings.
Training and Preparedness Programs
- Joint Training Sessions: Conducting workshops that include both EAP specialists and organizational staff to simulate crisis scenarios and response strategies.
- Skill Development: Training organizational leaders and managers on identifying signs of employee distress and effectively deploying EAP resources.
Evaluating and Adapting Strategies
- Continuous Improvement: Regular reviews of crisis response strategies and EAP effectiveness, making adjustments based on new insights and employee feedback.
- Innovation in Services: Encouraging innovation by integrating new psychological support technologies and methods into the EAP framework.
Enhancing EAP Effectiveness for Future Crises
Tailoring Services to Meet Emerging Needs
- Customization of Programs: Adapting EAP services to meet specific employee and organizational needs based on past crisis feedback and changing workplace dynamics.
- Technology Integration: Incorporating digital tools and platforms that enhance the accessibility and responsiveness of EAP services.
Training and Awareness Enhancement
- Regular Training Updates: Ensuring all employees are regularly trained on how to utilize EAP services effectively, with updates on any new features or protocols.
- Awareness Campaigns: Conducting ongoing awareness campaigns to keep mental health and EAP benefits at the forefront of organizational culture.
Feedback Mechanisms and Continuous Learning
- Structured Feedback Processes: Implementing structured feedback mechanisms to gather insights from employees about the effectiveness of the EAP during and after crises.
- Lessons Learned Sessions: Hosting regular ‘lessons learned’ sessions with EAP providers and organizational stakeholders to review responses to past crises and update procedures accordingly.
Proactive Innovations and Future Planning
- Innovative Practices: Exploring and adopting innovative practices in mental health support and crisis intervention.
- Future Scenario Planning: Engaging in scenario planning exercises to prepare for potential future crises, using insights gained from EAP interactions and feedback.
By continuously enhancing their services, seeking feedback, and adapting to new challenges, EAPs can maintain their relevance and effectiveness as critical components of organizational crisis management strategies.